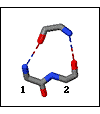
Beta Bulge
Definition
A motif of two consecutive residues (doubleton), a residue separate from these (singleton), and two H-bonds in which there is:
- H-bond between main-chain NH of the singleton and main-chain CO of second (C-terminal) residue of the doubleton
- H-bond between main-chain CO of the singleton and main-chain NH of first (N-terminal) residue of the doubleton
- βR conformation at the singleton and at the second (C-terminal) residue of the doubleton
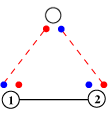
Sub-categories
In February 2019 we revised the sub-categories to include the conformation at residue ‘0’ — N-terminal to residue 1. This was because the conformation at this residue determines whether the Beta Bulge is of the ‘classic’ type or is a ‘G1α’ or ‘G1β’ Beta Bulge.
The base of the sub-categorization is between 1,2-αRβ (which include those designated ‘classic’) Beta Bulges and 1,2-αLβR (which include those designated ‘G1’).
- 0,1,2-αRαRβR
- 0,1,2-βRαRβR (classic)
- 0,1,2-αLαRβR
- 0,1,2-βLαRβR
- 0,1,2-αRαLβR (G1α)
- 0,1,2-βRαLβR (G1β)
- 0,1,2-αLαLβR
- 0,1,2-βLαLβR
The full classification also distinguishes between the possibilities that the singleton is N-terminal to (N-singleton) or C-terminal to (C-singleton) the doubleton for each of the above.
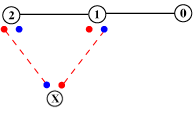
Alternative visualization
It is often convenient to present the β-bulge and its composites in a view that is flipped both vertically and horizontally from that above, with the singleton designated ‘X’ and the residue at position 0 included:
References
Richardson et. al, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 75:2574-2578 (1978)
Leader and Milner-White, Acta Cryst. D77 217–223 (2021)
Comments
1. This motif is also termed the ‘Narrow’ Beta Bulge.
2. A third hydrogen bond — from the singleton CO to the NH of residue-2 — is also frequently found.
Occurrence
1. The Beta Bulge is most often found at the edges of β-sheets, but its general location differs for the three main subcategories.
2. 0,1,2-αRαLβR (G1α) Beta Bulges are components of Beta Bulge Loops; 0,1,2-βRαLβR (G1β) Beta Bulges are components of Beta Links.