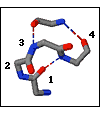
Beta Link
Definition
A motif of four consecutive residues (tetrapeptide), a residue separate from these (singleton), and three H-bonds in which there is:
- H-bond between the main-chain NH of residue-3 of the tetrapeptide and the main-chain CO of the singleton
- H-bond between the main-chain CO of residue-4 of the tetrapeptide and the main-chain NH of the singleton
- H-bond between the main-chain NH of residue-4 and the main-chain CO of residue-1 of the tetrapeptide
- βR conformation at residue-4 of the tetrapeptide
Show 3D view
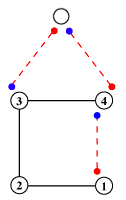
Sub-categories
The sub-categories distinguish the conformational variants of the Beta Turn, always found at residues-2 and -3, and whether the singleton is N-terminal (N-singleton) or C-terminal (C-singleton) to the tetrapeptide, primarily for analysis and graphical presentation.- 2,3-βRαL (N-singleton)
- 2,3-βRαL (C-singleton)
- 2,3-αLαL (N-singleton)
- 2,3-αLαL (C-singleton)
Alternative visualization
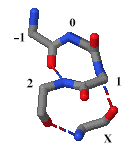
It is more usual to present the β-link in a way that relates to the β-bulge, rather than the β-turn. This involves replacing the numbering from 1-to-4 by –1-to-2, and flipping the diagram above vertically and horizontally, with the singleton designated ‘X’:
Show 3D view
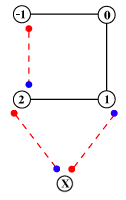
References
Leader and Milner-White, Acta Cryst. D77 217–223 (2021)
Leader and Milner-White, Acta Cryst. D77 1040–1049 (2021)
Comments
1. The Beta Link encompasses Beta Bulges of type 0,1,2-βRαLβR (G1β).
2. The Beta Link was previously listed here as ‘Beta Bulge Turn’ and then as ‘Beta Tether’.
Occurrence
Approx. 12% of Beta Bulges are parts of Beta Links.